-
Capabilities
- Processes Available
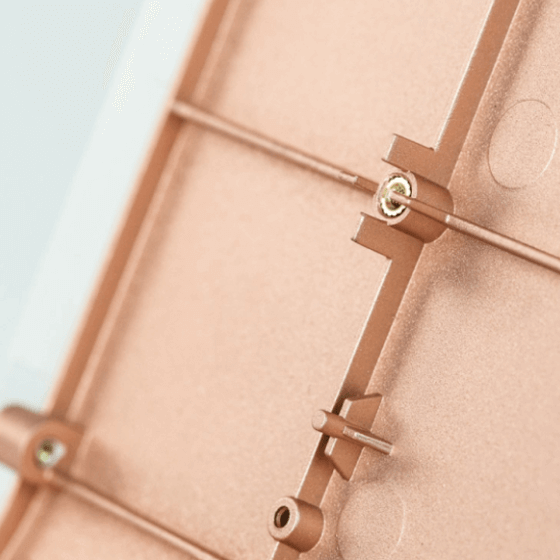
- CNC Machining Service
- CNC Milling
- CNC Turning
- Electrical Discharge Machining
- Metal
- All metal
- Aluminum
- Stainless steel
- Brass
- Copper
- Titanium
- Mild steel
- Alloy steel
- Tool steel
- Spring steel
- Processes Available
- Sheet Metal Fabrication Service
- Laser Cutting
- Bending
- Welding
- Plastic
- All plastic
- PMMA (Acrylic)
- Carbon Fiber
- Processes Available
- Injection Molding Service
- Injection Molding
- Overmolding
- Insert Molding
- Processes Available
-
Urethane Casting
(Vacuum Casting)
-
Industries
-
 Consumer electronics HOTFrom prototype to production to homes around the world
Consumer electronics HOTFrom prototype to production to homes around the world -
 Automotive HOTDrive product development and speed up innovation
Automotive HOTDrive product development and speed up innovation -
 Medical NEWAccelerating new product introduction for the medical industry
Medical NEWAccelerating new product introduction for the medical industry -
 Robotics NEWAccelerating new product introduction for the robotics industry
Robotics NEWAccelerating new product introduction for the robotics industry -
 Aerospace NEWGo from development to launch faster
Aerospace NEWGo from development to launch faster -
 Industrial machineryPower your machines with cutting-edge technologies
Industrial machineryPower your machines with cutting-edge technologies
-
- Resources
-
Company
- Feedback
- 3D models
Your Cart
Show up to the latest 200 orders
Data loading, please wait ...
Your cart is currently empty.
Get a quote
Subtotal
US $0
V0 Member 0% OFF
-US $0
Taxes ,coupon and reward points calculated in checkout
We accept all major credit cards
Total
$0
View Cart